© 2025 FilterCY
Submit an application
Fill the form and we will contact you as soon as possible
By clicking the Submit button, you agree to our Data Privacy
Find Your Perfect Reverse Osmosis Filter!
Answer a few quick questions, get a personalized recommendations for the best water filtration system for your home, and receive your personal discount!
Online. Free. Takes just 1 minute
Online. Free. Takes just 1 minute
How Drought Affects Tap Water Quality and the Role of Filtration in Protection
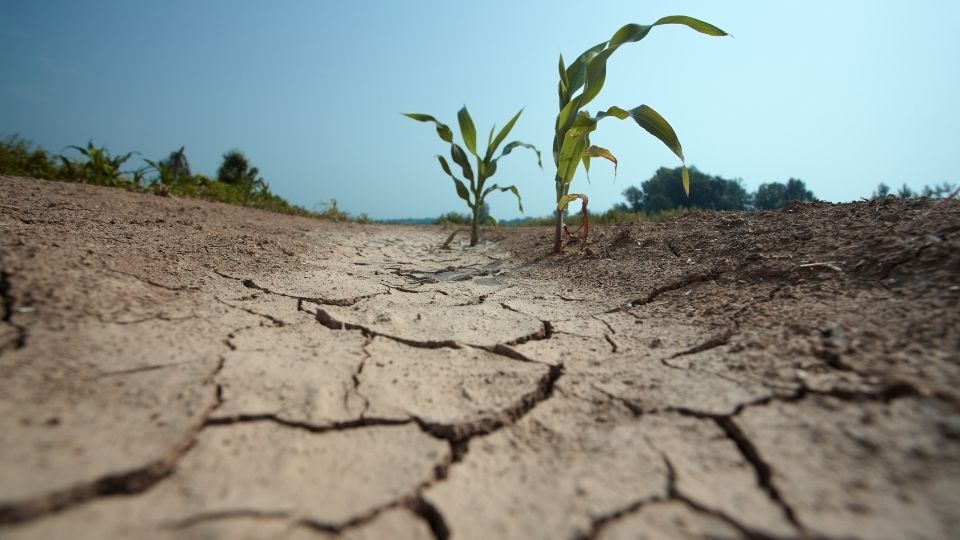

Drought has a significant impact on the quality of tap water, especially when reservoirs are the primary source. Here’s how it affects water quality:
1. Increased Concentration of Contaminants
As water levels drop, pollutants such as heavy metals, nitrates, pesticides, and organic compounds become more concentrated, making the water less diluted and potentially more harmful.
2. Growth of Bacteria and Algae
Drought leads to higher water temperatures and lower water levels, creating ideal conditions for algae blooms. This can result in toxins (such as microcystins), unpleasant odors, and poor-tasting water.
3. Higher Chlorine Levels and Byproducts
To compensate for declining water quality, treatment facilities may increase chlorine dosages, leading to the formation of disinfection byproducts like trihalomethanes, which can be harmful with prolonged exposure.
4. Increased Turbidity and Sediment Content
As water levels decrease, sediments and deposits from the reservoir floor can get stirred up, increasing turbidity and making purification more challenging.
5. Increased Salinity
In some regions, reduced freshwater inflow due to drought can allow saltwater intrusion into reservoirs, raising mineral content and affecting water taste.
How to Protect Yourself?
During drought conditions, using water filters is essential to remove chlorine, organic compounds, heavy metals, and unpleasant tastes. Reverse osmosis systems and carbon filters are among the best solutions to ensure clean and safe tap water.
1. Increased Concentration of Contaminants
As water levels drop, pollutants such as heavy metals, nitrates, pesticides, and organic compounds become more concentrated, making the water less diluted and potentially more harmful.
2. Growth of Bacteria and Algae
Drought leads to higher water temperatures and lower water levels, creating ideal conditions for algae blooms. This can result in toxins (such as microcystins), unpleasant odors, and poor-tasting water.
3. Higher Chlorine Levels and Byproducts
To compensate for declining water quality, treatment facilities may increase chlorine dosages, leading to the formation of disinfection byproducts like trihalomethanes, which can be harmful with prolonged exposure.
4. Increased Turbidity and Sediment Content
As water levels decrease, sediments and deposits from the reservoir floor can get stirred up, increasing turbidity and making purification more challenging.
5. Increased Salinity
In some regions, reduced freshwater inflow due to drought can allow saltwater intrusion into reservoirs, raising mineral content and affecting water taste.
How to Protect Yourself?
During drought conditions, using water filters is essential to remove chlorine, organic compounds, heavy metals, and unpleasant tastes. Reverse osmosis systems and carbon filters are among the best solutions to ensure clean and safe tap water.
BWT Water Filter Rental from €1/day
Enjoy clean and great-tasting water 24/7, save money, and forget about heavy bottles.
Choose your filter Not sure which water filter is right for you?
Take our quick quiz to discover the perfect solution tailored to your lifestyle and needs